Abstract
INTRODUCTION
Children with Down Syndrome (DS) and B-lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL) are at an increased risk of both relapse and treatment-related mortality, compared to those without DS. On COG study AALL1731 for de novo B-ALL, patients with DS and higher risk features (DS-High) are non-randomly treated with a regimen replacing intensive elements of conventional chemotherapy with three 28-day cycles of blinatumomab, with the combined goals of reducing toxicity and enhancing anti-leukemic efficacy. The DS-High group includes all NCI high risk (HR) patients; NCI standard risk (SR) patients with end-induction minimal residual disease positivity (>0.01%), unfavorable cytogenetics, CNS3 status, steroid pre-treatment, neutral cytogenetics with CNS2 status, or testicular disease. Neurotoxicity is a known risk of blinatumomab, with an incidence of 4% in block 1 and 1% in block 2 among pediatric patients with relapsed ALL (Brown et al, JAMA 2021). However, the specific risk in patients with DS has not been described to date. Here, we provide an early report of increased seizure incidence associated with blinatumomab in older DS-High patients enrolled on AALL1731 to date.
METHODS
We reviewed seizure incidence among patients with DS enrolled on AALL1731 from June 2019 to June 2021 who had proceeded to receive blinatumomab. Blinatumomab was administered at a dose of 15 mcg/m 2/day, using dexamethasone pre-medication in cycle 1. Infusions were interrupted for seizures, with resumption at 5 mcg/m 2/d permitted following full resolution for grade 1-3 seizures.
RESULTS
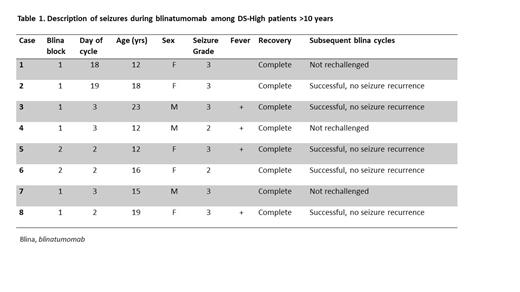
Among DS NCI HR patients, 8 of 47 (17%) had a seizure during blinatumomab infusion (Table 1). All 8 seizures occurred in patients over 10 years old. Six of the 8 seizures occurred in the first cycle of blinatumomab, most in the first 3 days of the infusion. Four had concomitant fever or cytokine release syndrome. Seizures were grade 2 (n=2) or grade 3 (n=6), and all resolved with full neurologic recovery. Of the 8 patients, 5 elected to resume blinatumomab; no further seizures occurred in these patients. There was no indication of increased seizure risk among NCI SR DS-High patients (1 seizure among 11 patients), or among DS or non-DS patients receiving blinatumomab on other study strata (0 of 7 DS SR-Avg; 1 of 146 non-DS SR-Avg; and 2 of 120 non-DS SR-High).
CONCLUSIONS
The incidence of seizures associated with blinatumomab in DS-ALL patients older than 10 years appears higher than previously reported in children without DS. The majority of seizures occurred within the first 3 days, all fully resolved with no sequelae, and no patient who resumed blinatumomab infusion at a lower rate experienced further seizures. Seizure prophylaxis may be advisable in DS patients while receiving blinatumomab, particularly those >10 years of age. Further follow-up and a larger sample size are needed to confirm incidence and identify risk factors predisposing DS patients to neurologic toxicity.
Li: Novartis Canada: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Raetz: Pfizer: Research Funding; Celgene: Other: DSMB member. Loh: MediSix therapeutics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Gupta: Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Rau: Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Advisory Board; AbbVie Pharmaceuticals: Other: Spouse is employee and stock holder; Servier Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy.
This trial includes the use of blinatumomab in combination with chemotherapy for treatment of de novo B-lymphoblastic leukemia.